
A selenium speciation machine can measure the amount of selenium present. Some semimetals like selenium and arsenic can be toxic. Germanium is heavily used in the semiconductor industry. They act as metals when reacting with halogens, and as non-metals when reacting with alkali metals.
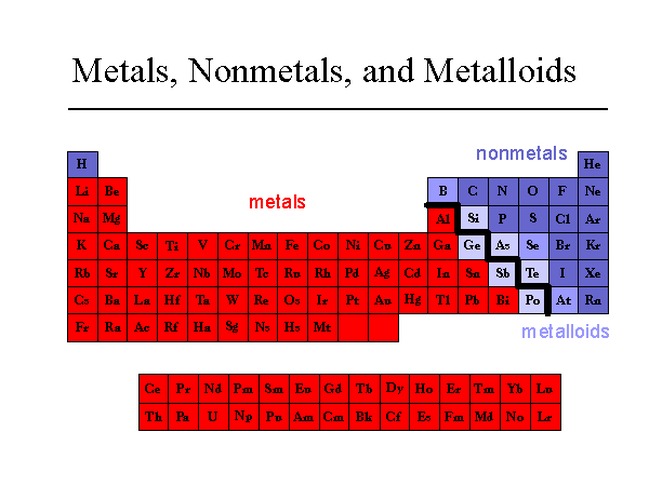
Most form several different anions with oxygen that make a variety of salts with metals, although the aqueous chemistry of germanium is more limited. Metalloids generally have chemical properties similar to non-metals. Semi-conductors are capable of conducting electricity better than insulator, but not as well as conductors. They are brittle, and are typically semi-conductors. Some forms of selenium have an amazing, almost space-like sheen. Metalloids can be shiny or dull, but usually have a metallic luster. Semimetals, also known as metalloids, have properties of both metals and non-metals. Most of non-metals exist in two of the three states of matter at room temperature: gases and solids, except bromine, which exists as a liquid. They tend to have lower melting points than metals. In general, non-metals are brittle, dull, and poor conductors of heat and electricity. Thus, they are electronegative elements with high ionization energies. Nonmetals are elements that form negative ions by gaining electrons during chemical reactions. Most metals are silvery, although some like gold, cesium and copper are colored.Tungsten, platinum, osmium, gold and iridium are extremely dense. Metals exhibit a wide range of densities, but generally are more dense than nonmetals.However, most boiling points are still quite high. Melting point of metals: Metals often have high melting and boiling points, but there are many exceptions to the melting point, like cesium, gallium, mercury, rubidium and tin which all have fairly low melting points.Forming cations in aqueous solution by losing their electrons.Being ductile – which means it can be drawn into a wire.Gold is the most malleable of all the metals Some metals will form a patina and the luster is lost. Having a luster (shine) from reflecting light.Special groups of metals include the noble metals Ru, Rh, Pd, Pt, Au, Os, Ir, Ag and the refractory metals Nb, Mo, Ta, W and Re. Metals exhibit a wide range of reactivity. Most metals form at least one basic oxide, although some are amphoteric. Metals generally form ionic bonds with nonmetals, but there are exceptions. All metals are solids at room temperature, except mercury which is a liquid. Metals are also good conductors of heat and electricity. Furthermore, they are ductile, malleable, and lustrous. Most metals share the properties of being shiny, very dense, and having high melting points. Thus, they are electropositive elements with low ionization energies. Metals are elements that form positive ions by losing electrons during chemical reactions, except hydrogen. Nonmetals are generally on the upper right side of the periodic table, metals cover most of the remaining area with metalloids in-between them. Elements are further classified into metals, non-metals, and metalloids (semimetals).
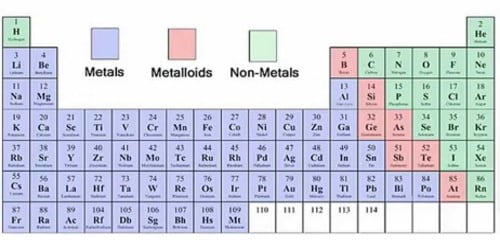
In other words, an element is the simplest form of matter. Luster – the quality of reflecting light from the surface and can be polished Introduction to Metals, Metalloids, and NonmetalsĪn element is a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substance. Malleability – the ability to be hammered into thin sheets Topics Covered in Other Articlesĭuctility – the ability to be drawn into wires For example, laxatives and antacids use magnesium, and it is also used to stabilize abnormal blood vessel spasms or nerve excitation.In this tutorial, you will learn about the properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids (semimetals) as well as examples of metal elements, and nonmetal elements. The element is also used for medicinal purposes.

Magnesium ions interact with compounds like DNA, RNA and ATP. In fact, by mass, the element is the 11th most abundant element in the human body. The other non-metals are solids at room temperature, including carbon and sulphur. One non-metal, bromine, is a liquid at room temperature. Some examples are Iron(Fe,) Aluminum(Al), Copper(Cu), Cobalt(Co), Zinc. In humans, Magnesium ions are essential to various functions in all cells. Metals are elements which give cations (positive ions) naturally, (except for H). Magnesium makes up 13 percent of the Earth’s mass. While magnesium only occurs naturally in combination with other elements, it remains the ninth most abundant element in the universe, the eighth most abundant in the Earth’s crust and the fourth most common element in the Earth itself. Once lit, it is difficult to extinguish as it can burn in nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water. It is highly flammable, especially when shaved or in the form of a powder. As a solid, the element has a shiny, gray appearance, which is one of the characteristics of elements in the metal group on the periodic table. The chemical symbol of magnesium is Mg, and it has an atomic number of 12.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
